Strategic Rationale for M&A
Strategic rationale answers the fundamental question: "Why should we pursue this acquisition?" It articulates how the deal aligns with corporate strategy and creates value beyond what could be achieved organically.
What is Strategic Rationale?
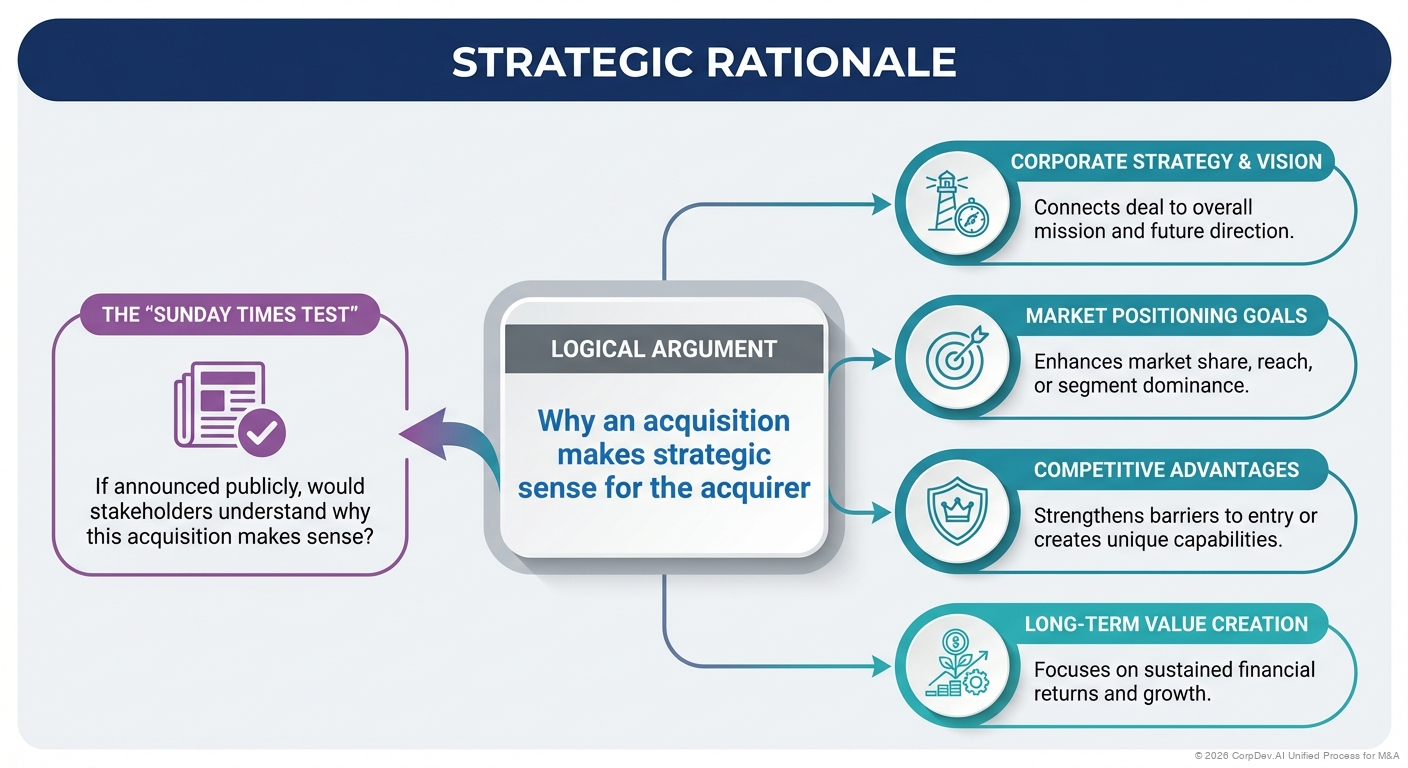
Strategic rationale is the logical argument that explains why an acquisition makes strategic sense for the acquirer. It connects the deal to:
- Corporate strategy and vision
- Market positioning goals
- Competitive advantages
- Long-term value creation
A compelling strategic rationale should pass the "Sunday Times Test": If announced publicly, would stakeholders understand why this acquisition makes sense?
Core Components
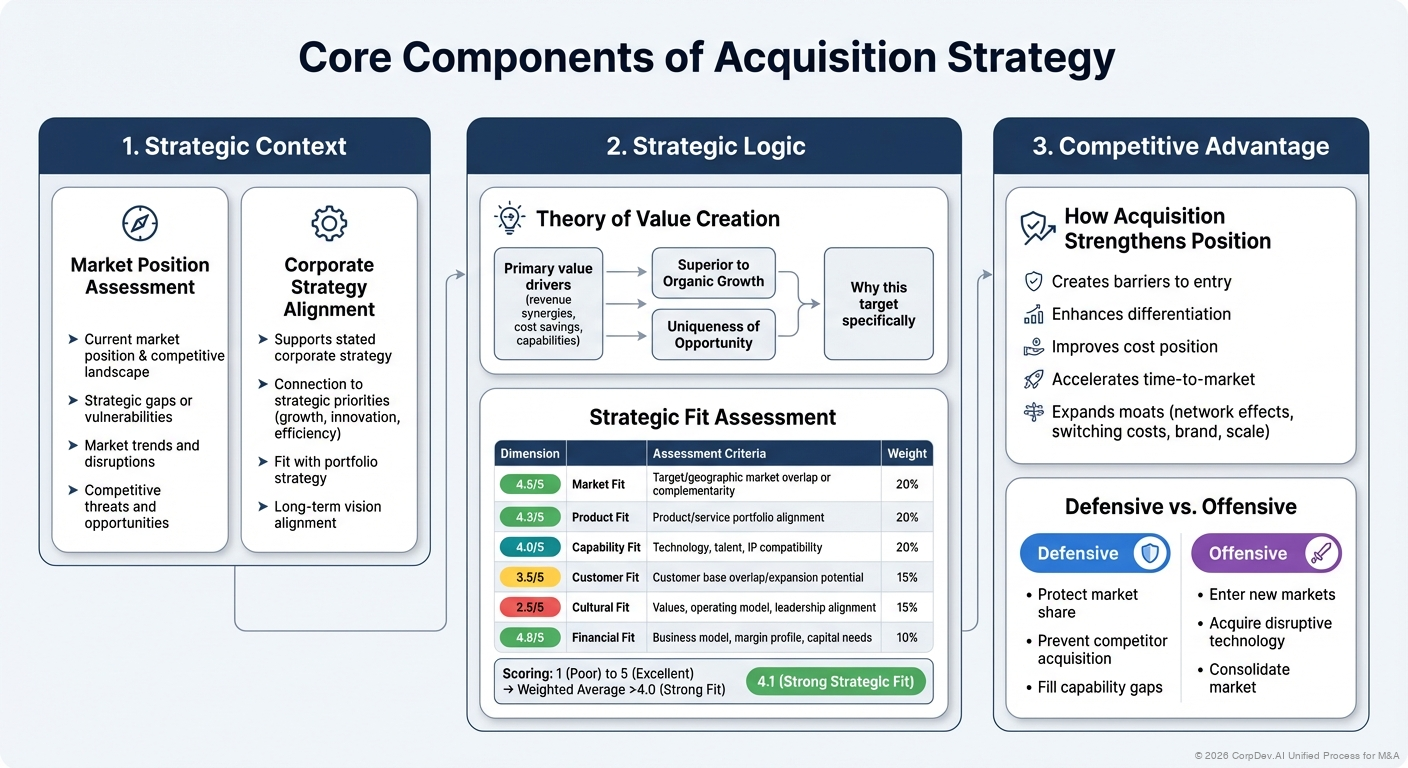
1. Strategic Context
Market Position Assessment
- Current market position and competitive landscape
- Strategic gaps or vulnerabilities
- Market trends and disruptions
- Competitive threats and opportunities
Corporate Strategy Alignment
- How acquisition supports stated corporate strategy
- Connection to strategic priorities (growth, innovation, efficiency)
- Fit with portfolio strategy
- Long-term vision alignment
2. Strategic Logic
Theory of Value Creation
- Primary value drivers (revenue synergies, cost savings, capabilities)
- Why acquisition is superior to organic growth
- Why this target specifically (vs. alternatives)
- Uniqueness of opportunity
Strategic Fit Assessment
| Dimension | Assessment Criteria | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fit | Target/geographic market overlap or complementarity | 20% |
| Product Fit | Product/service portfolio alignment | 20% |
| Capability Fit | Technology, talent, IP compatibility | 20% |
| Customer Fit | Customer base overlap/expansion potential | 15% |
| Cultural Fit | Values, operating model, leadership alignment | 15% |
| Financial Fit | Business model, margin profile, capital needs | 10% |
Scoring: 1 (Poor) to 5 (Excellent) → Weighted average should be >4.0 for strong strategic fit
3. Competitive Advantage
How Acquisition Strengthens Position
- Creates barriers to entry
- Enhances differentiation
- Improves cost position
- Accelerates time-to-market
- Expands moats (network effects, switching costs, brand, scale)
Defensive vs. Offensive
- Defensive: Protect market share, prevent competitor acquisition, fill capability gaps
- Offensive: Enter new markets, acquire disruptive technology, consolidate market
Strategic Archetypes
Choose the primary strategic rationale that best describes the acquisition:
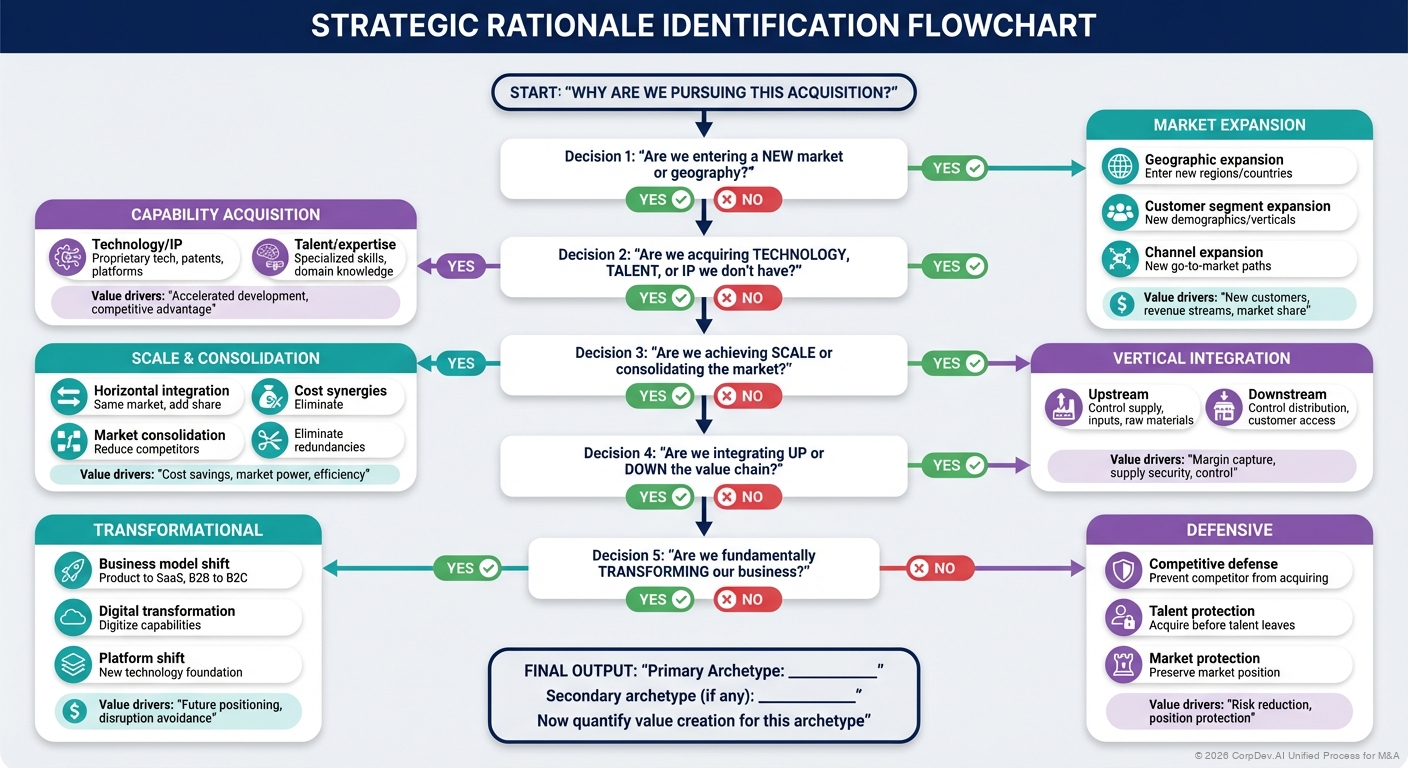
1. Market Expansion
Geographic Expansion
- Enter new regions or countries
- Acquire local presence and distribution
- Gain regulatory licenses or market access
Customer Segment Expansion
- Reach new customer demographics
- Move upmarket or downmarket
- Cross-sell to new industries
Channel Expansion
- Add direct-to-consumer capability
- Acquire distribution networks
- Enter new go-to-market channels
"Acquiring [Target] provides immediate access to the European market with established customer relationships, regulatory approvals, and local distribution infrastructure that would take 3-5 years to build organically."
2. Capability Acquisition
Technology & IP
- Acquire proprietary technology or patents
- Accelerate product roadmap
- Access R&D capabilities
Talent & Expertise
- Acquire specialized skills or domain expertise
- Build new organizational capabilities
- Gain thought leadership
Data & Insights
- Access unique datasets
- Acquire AI/ML models
- Gain customer intelligence
"[Target]'s AI-powered recommendation engine represents 3 years of R&D investment and patent-protected algorithms. Acquiring this technology immediately positions us as market leader in personalization, 18-24 months ahead of organic development timeline."
3. Scale & Consolidation
Horizontal Integration
- Increase market share
- Achieve economies of scale
- Consolidate fragmented market
Cost Synergies
- Reduce redundant costs
- Increase purchasing power
- Optimize operations
"Combining operations creates the #2 player in the industry with 23% market share, generates $150M in annual cost synergies through facility consolidation and purchasing power, and provides scale to compete with the market leader."
4. Vertical Integration
Upstream Integration
- Control supply chain
- Secure critical inputs
- Improve margins
Downstream Integration
- Direct customer access
- Control distribution
- Capture more value chain
"Acquiring our largest component supplier secures supply of critical technology, reduces COGS by 15%, and provides $200M annual margin improvement while eliminating supply chain risk that disrupted production in 2024."
5. Product Portfolio Enhancement
Product Line Extension
- Fill gaps in product portfolio
- Complete end-to-end offering
- Bundle complementary products
Innovation Acceleration
- Acquire next-generation products
- Enter adjacent markets
- Refresh legacy portfolio
"[Target]'s cloud security platform completes our end-to-end cybersecurity suite, enabling us to compete for enterprise-wide contracts worth $500M+ that require comprehensive solutions."
6. Transformation & Disruption
Business Model Transformation
- Shift from product to SaaS
- Move from B2B to B2C
- Transition to platform model
Digital Transformation
- Acquire digital capabilities
- Modernize technology stack
- Build data/analytics infrastructure
"Acquiring [SaaS Target] accelerates our transition from perpetual license to subscription model, immediately providing cloud infrastructure, customer portal, and recurring revenue base that de-risks our 3-year transformation plan."
Building Strategic Rationale: Framework
Step 1: Define Strategic Objectives
Ask:
- What are our top 3 strategic priorities for the next 3-5 years?
- What are our biggest strategic gaps or vulnerabilities?
- What capabilities or market positions do we need to win?
Document:
Strategic Priority #1: [e.g., "Become market leader in AI-powered solutions"]
- Current gap: [e.g., "Limited AI/ML capabilities, weak data infrastructure"]
- Target state: [e.g., "Industry-leading AI platform with 40%+ of revenue AI-enabled"]
- Timeline: [e.g., "Achieve by 2027"]
Step 2: Evaluate Build vs. Buy
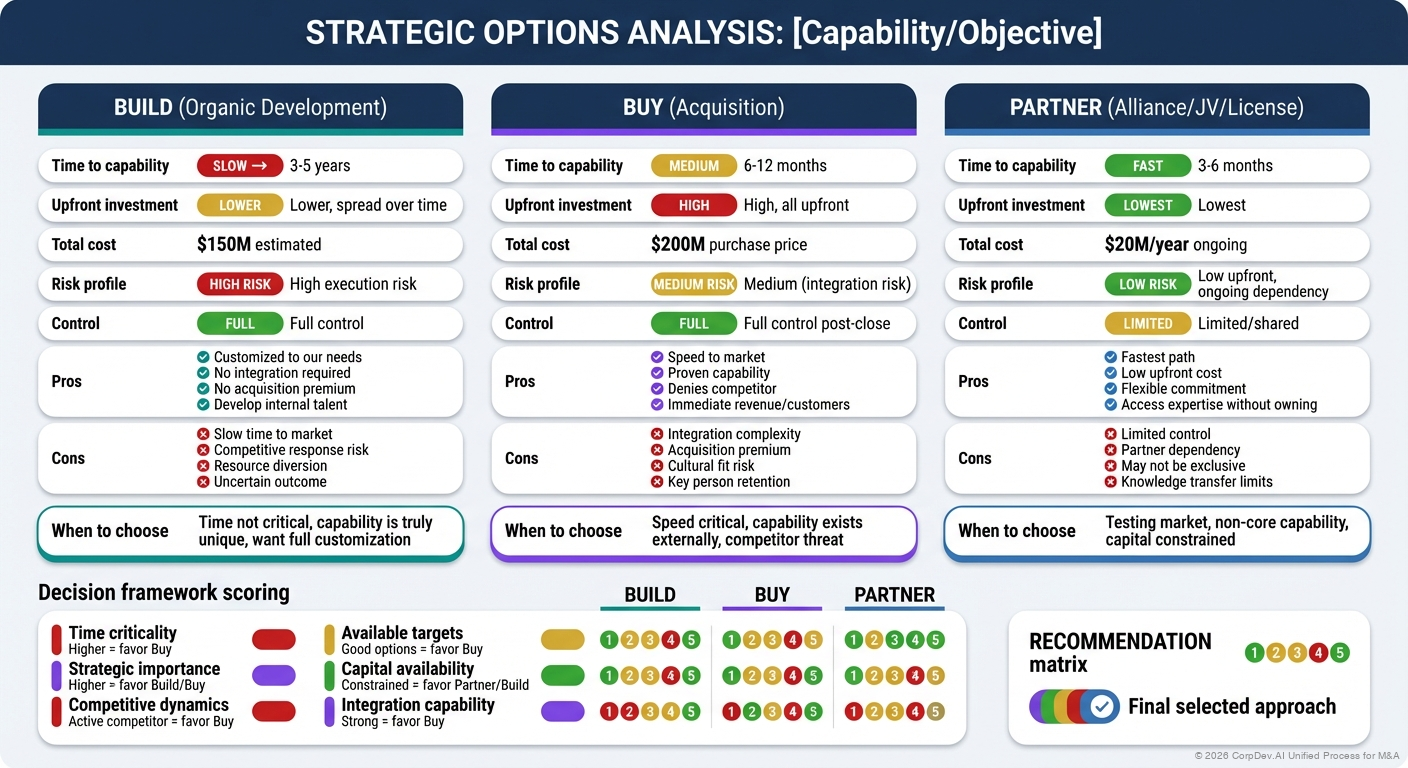
Build (Organic)
| Factor | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Time required | [years] |
| Investment needed | [$M] |
| Success probability | [%] |
| Key risks | [list] |
Buy (Acquisition)
| Factor | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Time to close | [months] |
| Acquisition cost | [$M] |
| Integration complexity | [Low/Med/High] |
| Key risks | [list] |
Decision Matrix
- Speed: How urgently do we need this capability?
- Risk: What's the probability of successful organic development?
- Cost: What's the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each option?
- Competitive Dynamics: Will competitors move first?
Acquisition when: time-to-market is critical, organic development risk is high, target has unique/scarce assets, competitors may acquire target, or market window is closing.
Step 3: Articulate "Why This Target"
Unique Attributes
- What makes this target special vs. alternatives?
- What competitive advantages or assets are unique?
- Why is this the best/only option?
Alternative Analysis
| Alternative | Pros | Cons | Why Not Chosen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target A | [strengths] | [weaknesses] | [rationale] |
| Target B | [strengths] | [weaknesses] | [rationale] |
| Organic | [strengths] | [weaknesses] | [rationale] |
Step 4: Quantify Strategic Value
Revenue Impact
- Market expansion: $[X]M new addressable market
- Cross-sell/upsell: $[X]M incremental revenue
- Faster time-to-market: $[X]M revenue acceleration
Cost Impact
- Synergies: $[X]M annual cost reduction
- Efficiency gains: $[X]M operational improvement
- Avoided costs: $[X]M saved vs. organic investment
Intangible Value
- Competitive positioning improvement
- Risk reduction (supply chain, technology, competitive)
- Strategic optionality (future M&A, product development)
Step 5: Connect to Value Creation
Value Creation Linkage
Strategic Rationale → Value Driver → Financial Impact
Example:
"Acquire market-leading AI technology" →
"Enable AI features in 80% of products" →
"$250M revenue increase + 500bps margin expansion = $400M NPV"
Strategic Rationale Checklist
Compelling Strategic Rationale Has:
- Clear connection to stated corporate strategy and priorities
- Specific answer to "why now?" (market timing, competitive dynamics)
- Articulated advantages of acquisition vs. organic development
- Unique value of this specific target vs. alternatives
- Quantified impact on strategic objectives (market share, capabilities, etc.)
- Risk mitigation addressing key strategic vulnerabilities
- Competitive analysis showing how deal strengthens position
- Stakeholder alignment that board/executives understand and support
- Integration feasibility demonstrating deal is executable
- Long-term vision connecting to 5+ year corporate direction
Common Pitfalls
❌ Weak Strategic Rationale
"We're buying revenue"
- Growth for growth's sake without strategic logic
- No clear path to profitable integration
- Missing competitive advantage story
"We're diversifying"
- Conglomerate discount typically destroys value
- Lack of strategic fit or synergy potential
- Management distraction risk
"We have extra cash"
- Financial capacity is not strategic rationale
- Alternative uses (buybacks, dividends) may be better
- Implies lack of strategic discipline
"Everyone else is doing it"
- Herd mentality leads to overpaying
- Industry consolidation isn't always value-creating
- Must have unique thesis for this specific deal
✓ Strong Strategic Rationale
Passes the "So What?" Test
- Clearly articulates impact on competitive position
- Specific about how value is created
- Differentiates from alternatives
Backed by Evidence
- Market analysis supporting strategic thesis
- Customer validation of strategic fit
- Financial modeling quantifying value
Executable
- Realistic integration plan
- Identified synergy capture mechanisms
- Clear ownership and accountability
Strategic Rationale Template
## Strategic Rationale: [Deal Name]
### Executive Summary
[2-3 sentences summarizing why this acquisition makes strategic sense]
### Strategic Context
**Current Position**: [Where we are today]
**Strategic Gap**: [What we're missing]
**Market Opportunity**: [What the market offers]
**Competitive Dynamics**: [What competitors are doing]
### Strategic Logic
**Primary Archetype**: [e.g., Capability Acquisition - Technology]
**Why This Deal**:
1. [First strategic reason with quantification]
2. [Second strategic reason with quantification]
3. [Third strategic reason with quantification]
### Why Now
- [Time-sensitive factor #1]
- [Time-sensitive factor #2]
- [Competitive/market dynamics]
### Why This Target
**Unique Attributes**:
- [What makes this target special]
- [Competitive advantages]
- [Scarce/irreplaceable assets]
**vs. Alternatives**:
- Build: [Why not organic] → [time/risk/cost rationale]
- Target B: [Why not alternative] → [fit/capability rationale]
- Partner: [Why not JV/partnership] → [control/integration rationale]
### Strategic Fit Assessment
| Dimension | Score | Rationale |
|-----------|-------|-----------|
| Market Fit | [1-5] | [explanation] |
| Product Fit | [1-5] | [explanation] |
| Capability Fit | [1-5] | [explanation] |
| Customer Fit | [1-5] | [explanation] |
| Cultural Fit | [1-5] | [explanation] |
| Financial Fit | [1-5] | [explanation] |
| **Weighted Average** | **[X.X]** | |
### Value Creation Linkage
Strategic Rationale → Value Driver → Quantified Impact
[Example]:
Acquire AI technology → Enable predictive analytics → $200M revenue
Gain European presence → Access 500M market → $150M revenue
Vertical integration → 15% margin improvement → $100M EBITDA
### Competitive Advantage
**How This Deal Strengthens Our Position**:
1. [Competitive advantage #1]
2. [Competitive advantage #2]
3. [Competitive advantage #3]
**Defensive/Offensive**:
- [Describe whether primarily defensive or offensive and why]
### Risks & Mitigants
| Strategic Risk | Probability | Impact | Mitigation |
|----------------|-------------|--------|------------|
| [Risk #1] | [H/M/L] | [H/M/L] | [Plan] |
| [Risk #2] | [H/M/L] | [H/M/L] | [Plan] |
### Strategic Metrics
**Success Measures (12-24 months post-close)**:
- [ ] [Strategic KPI #1 with target]
- [ ] [Strategic KPI #2 with target]
- [ ] [Strategic KPI #3 with target]
### Board/IC Summary
[2-3 sentences articulating strategic rationale for approval presentation]
"This acquisition [primary archetype] by [specific action], enabling us to [strategic outcome]. Combined with [acquirer], we will [competitive position], creating [value quantification] in value through [key drivers]."
Examples by Industry
Technology
SaaS Acquisition
- Rationale: Accelerate cloud transition, acquire recurring revenue base
- Value: Subscription model, customer relationships, cloud infrastructure
- Metric: ARR growth, customer retention, platform adoption
AI/ML Acquisition
- Rationale: Acquire proprietary algorithms, talent, training data
- Value: Time-to-market acceleration, IP protection, capability gap fill
- Metric: AI feature adoption, model accuracy, patent portfolio
Healthcare/Life Sciences
Medical Device Acquisition
- Rationale: Complete product portfolio, enter new specialty, geographic expansion
- Value: Regulatory approvals, clinical data, physician relationships
- Metric: Revenue per physician, procedure volume, market share
Biotech Acquisition
- Rationale: Acquire drug pipeline, R&D capabilities, therapeutic expertise
- Value: Clinical assets, patent protection, time-to-market
- Metric: Pipeline value, probability of success, launch timeline
Industrial/Manufacturing
Supplier Acquisition
- Rationale: Vertical integration, supply chain security, margin improvement
- Value: Cost reduction, quality control, capacity assurance
- Metric: COGS reduction, on-time delivery, defect rates
Consolidation Play
- Rationale: Scale economies, market share, operational efficiency
- Value: Fixed cost leverage, purchasing power, pricing power
- Metric: Market share, EBITDA margin, capacity utilization
Best Practices
1. Start with Strategy, Not the Deal
- Develop strategic rationale before engaging with target
- Ensure deal serves strategy, not vice versa
- Walk away if strategic fit weakens during diligence
2. Be Specific and Quantified
- Vague rationale ("strengthen market position") is unconvincing
- Quantify impact on key metrics
- Provide evidence and data supporting thesis
3. Test with Skeptics
- Present rationale to board/IC members who will challenge
- Stress-test assumptions with outsiders
- Incorporate feedback and address concerns head-on
4. Connect to Financial Returns
- Strategic rationale must translate to financial value
- Show clear path from strategy to cash flows
- Demonstrate ROIC exceeds cost of capital
5. Plan for Communication
- Craft narrative for employees, customers, investors
- Anticipate questions and objections
- Prepare executives to articulate rationale consistently
Related Resources
- Deal Thesis Overview - Comprehensive deal thesis framework
- Business Case Development - Financial justification and ROI analysis
- Value Creation Planning - Capturing synergies and strategic value
- M&A Strategy Development - Corporate development strategy frameworks
Key Takeaways
- Strategic rationale is the "why" - it must clearly answer why this acquisition serves corporate strategy
- Choose one primary archetype - focus strategic message rather than claiming all benefits
- Be specific about "why this target" - articulate unique value vs. alternatives
- Quantify strategic value - connect qualitative rationale to financial impact
- Test build vs. buy - justify why acquisition beats organic development
- Pass the "Sunday Times Test" - rationale should make sense to external stakeholders
- Avoid weak rationale - "buying revenue," "diversification," or "we have cash" aren't strategic
A compelling strategic rationale is clear, specific, evidence-based, and connects acquisition to long-term corporate strategy and competitive advantage. It should be simple enough to explain in 2-3 sentences, yet detailed enough to withstand board scrutiny.
© 2026 CorpDev.Ai Unified Process for M&A
Last updated: Thu Oct 30 2025 20:00:00 GMT-0400 (Eastern Daylight Time)